What is Arthritis?
Type, Cause, Symptoms & Cure
Arthritis is an inflammation of the joints. It can affect one joint or multiple joints. There are many different types of arthritis, with different causes and treatment methods. Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis.
Other common include:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Gout.
The symptoms of arthritis usually develop over time, but they may also appear suddenly. The typical age for developing rheumatoid arthritis is between ages 30 and 50. It can, however, affect children, teens, and younger adults.
Osteoarthritis commonly develops after the age 50 or 60 years, but there are studies that reveal evidence of occurring this in women in their 40s. It also tends to be more prevalent in individuals who are overweight.
Joint pain, stiffness, and swelling are the most common symptoms of arthritis. Your symptoms may also feel worse in the morning when you get out of bed or upon standing up after you’ve been resting.
Symptoms of Osteoarthritis include:
- limited range of motion that sometimes goes away after movement
- clicking or popping with bending
- muscle weakness around the joint
- instability or buckling of the joint
- bony growths in the fingers
- grating or scraping feeling in the knees
Symptoms of Rheumatoid arthritis include:
- Morning stiffness that can last 30 minutes or more
- More than one affected joint
- Onset in smaller joints like feet and hands
- Same joints on both sides of the body are affected
- Fatigue
- Low-grade fever
- Inflammation of the eyes and mouth
- Inflammation of the heart muscle and blood vessels
- Low red blood cell count
Arthritis may be caused by:
- Wear and tear of a joint from overuse
- Age (Most common in adults over age 50)
- Injuries
- Obesity
- Autoimmune disorders
- Genes or family history
- Muscle weakness
Osteoarthritis
Normal wear and tear causes Osteoarthritis, one of the most common forms of arthritis. An infection or injury to the joints can exacerbate this natural breakdown of cartilage tissue.
Cartilage is a firm but flexible connective tissue in your joints. It protects the joints by absorbing the pressure and shock created when you move and put stress on them. A reduction in the normal amount of this cartilage tissue causes some forms of arthritis.
Your risk of developing Osteoarthritis may also be higher if you have a family history of the disease.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Another common form of arthritis, Rheumatoid arthritis, is an autoimmune disorder. It occurs when your body’s immune system attacks the tissues of the body, resulting in inflammation to joints as well as other body organs.
In the joints, this inflammatory response affects the synovium, a soft tissue in your joints that produces a fluid that nourishes the cartilage and lubricates the joints, eventually destroying both bone and cartilage inside the joint.
The exact cause of the immune system’s attacks is unknown. But scientists have discovered genetic markers that increase your risk of developing this.
Seeing your primary care physician is a good first step if you’re unsure who to see for an arthritis diagnosis. They will perform a physical exam to check for fluid around the joints, warm or red joints, and document the range of motion in the joints. Your doctor can refer you to a specialist if needed.
If you’re experiencing severe symptoms, you may choose to schedule an appointment with a rheumatologist first. This may lead to a faster diagnosis and treatment.
Documenting inflammation levels in your blood and aspirating and analyzing joint fluids, if present, can help your doctor determine what kind of arthritis you have.
Blood tests that check for specific types of antibodies like anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP), rheumatoid factor (RF) and antinuclear antibody (ANA) are also common diagnostic tests.
Doctors commonly use imaging scans such as X-ray, MRI, and CT scans to produce an image of your bones and cartilage. This helps them rule out other causes of your symptoms, such as bone spurs.
How Arthritis is Cured
The main goal of treatment is to reduce the amount of pain you’re experiencing and prevent additional damage to the joints.
In general, treatment for arthritis involves a combination of:
- Medications and supplements
- Physical therapy
- Nutrient-rich diet
- Regular exercise
- Weight loss, if needed
- Mobility assistance devices, such as canes or walkers
Improving your joint function is also important. Your doctor may prescribe a combination of treatment methods to achieve the best results.
What lifestyle changes can help people with Arthritis?
Losing any excess weight and maintaining a moderate weight reduces the risk of developing Arthritis and can reduce symptoms if you already have the condition.
Eating a nutritious diet is important for weight loss. Choosing a diet with lots of antioxidants, such as fresh fruits, vegetables, and herbs, can help reduce inflammation. There is no specific diet that treats arthritis, but some types of food may help reduce inflammation. The following foods can provide many nutrients that are good for joint health:
- Fish
- Nuts and seeds
- Fruits and vegetables
- Beans
- Olive oil
- Whole grains
Foods that should be limited or avoided if you have arthritis include:
- Fried foods
- Processed foods
- Dairy products
- A high intake of meat
Self-Management
Self-management of arthritis symptoms is also important.
Regular exercise can keep your joints flexible. Swimming is often a good form of exercise for people with arthritis because it does not put pressure on your joints the way running and walking do. Staying active is important, but listening to your body when it’s resting and avoiding overexerting yourself are just as essential.
At-home exercises you can try include:
- the head tilt, neck rotation, and other exercises to relieve pain in your neck
- finger bends and thumb bends to ease pain in your hands
- leg raises, hamstring stretches, and other easy exercises for knee arthritis.
- Staying physically active
- Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight
- Getting regular check-ups with the doctor
- Protecting joints from unnecessary stress
Ayurvedic Treatment For Arthritis
Ayurvedic treatment for arthritis that We offer at VAID RUBAL`S CLINIC
focuses on removing toxins from the joints, balancing the vata
dosha (Vata dosha is mainly responsible for joint problems) and strengthening
your bones from within.
Ayurveda takes a comprehensive approach to treat any disorder. At VAID RUBAL`S CLINIC, We go to the root cause of your illness, understand your body constitution and lifestyle, medical history, mental state, etc. to suggest a holistic, personalized Ayurvedic treatment for different body types and ailments. We prescribe diet and lifestyle modifications along with natural Ayurvedic remedies.
Studies have shown that Usually, majority of people visit an Ayurvedic practitioner when their disease has already progressed to the last stage or an a complicated
state and everything else has failed in protecting their joints from
deteriorating.
We strongly believe that, When Ayurveda is the first choice for treatments and not a last option, the results are quicker, better and long-lasting. Painkillers are good for subsiding the pain but if you want safe and effective relief in your condition, Ayurveda is the only best solution.
So, why wait for the symptoms to flare up when you can strengthen your
joints from within and treat the condition in an effective way. You can
consult us over a video call, phone call or visit your
nearest location for the treatment as per your convenience. We’ll be happy to be a part of your treatment journey while you achieve A balanced and good health with the help of Ayurveda.
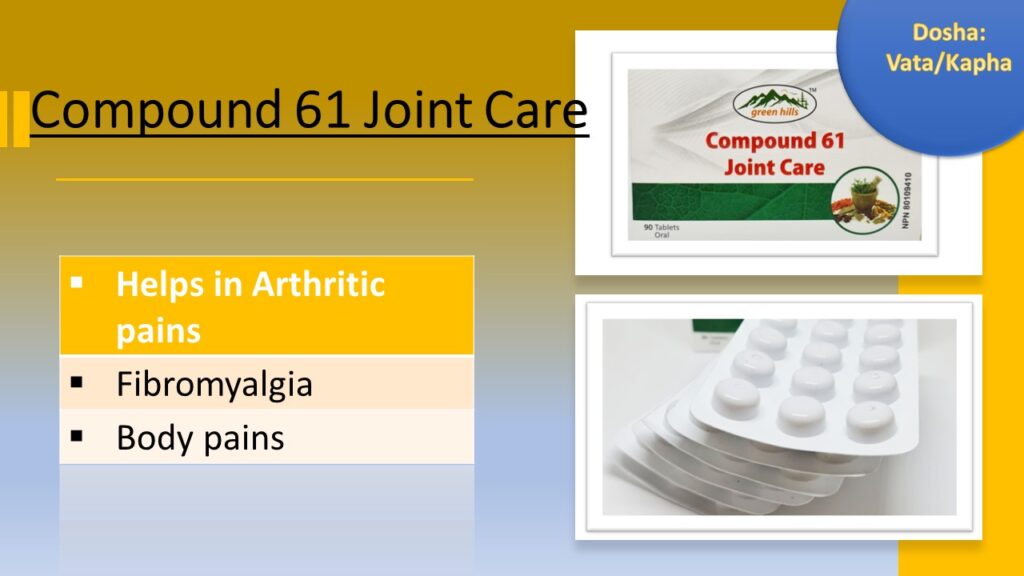
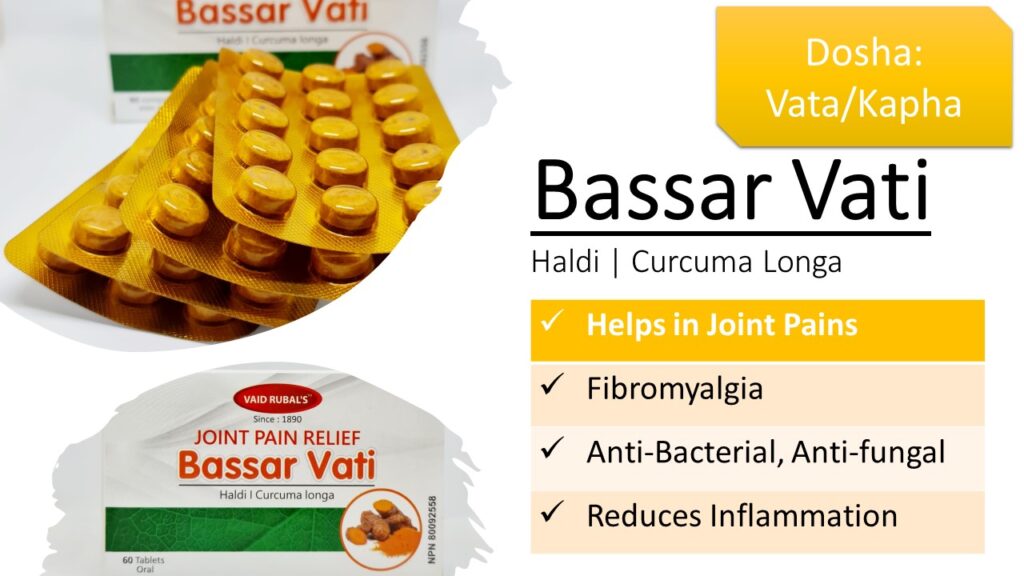
Vaid Rubal's Special Formula For Arthritis